In the evolving landscape of edible oil production, choosing the optimal extraction method directly influences oil yield, nutritional value, energy efficiency, and overall product quality. This article presents an in-depth comparison between cold-press and hot-press oil extraction processes, supported by relevant data and real-world cases. The aim is to equip small to medium-sized edible oil manufacturers with the insights necessary for scientifically sound process decisions, balancing production efficiency with product excellence.
Both cold-press and hot-press are mechanical extraction methods employed in oilseed processing, differing primarily in temperature control and operational approach.
The primary distinction between the two methods lies in the trade-off between preserving nutritional integrity and maximizing extraction yield:
| Criteria | Cold-Press | Hot-Press |
|---|---|---|
| Typical Operating Temperature | <50°C | 90–130°C |
| Nutritional Component Retention | >90% (Vitamin E, polyphenols preserved) | ~70–75% (Thermal degradation risk) |
| Oil Yield (%) | 30–38% | 45–55% |
| Energy Consumption (kWh/ton) | 400–600 | 650–850 |
As the data suggests, hot-pressing significantly increases oil extraction efficiency by approximately 15–20% compared to cold-pressing but at the cost of reduced retention of heat-sensitive bioactive compounds. For producers emphasizing premium, health-oriented oils, cold-press remains preferable; conversely, hot-pressing supports higher volume operations targeting mainstream markets.
Beyond yield and nutrition, practical factors affect process selection:
These factors translate to distinct maintenance costs and operational workflows, influencing total cost of ownership (TCO) over time.
For small-scale, artisanal edible oil producers aiming to highlight organic, raw, and nutrient-rich oils, cold-press extraction ensures product differentiation despite lower yields. Integration of compact, automated cold-press machines can optimize labor efficiency while retaining premium characteristics.
Mid-sized enterprises focused on balancing output volume with quality may benefit from hybrid approaches or novel technologies such as combined cold and hot pressing systems—initial cold pressing to preserve nutrients followed by a gentle heat stage to recover residual oil—improving overall recovery rates up to 50% while maintaining an acceptable nutrient profile.
Large-scale producers targeting commodity edible oils typically standardize hot-press extraction for maximum throughput and cost efficiency, leveraging economies of scale.
To further streamline production and combine the advantages of both extraction methods, advanced fully automated cold and hot press oilseed pressing machines have emerged. These units feature process precision, optimized energy consumption, and adaptive technology suited for diverse oilseed types—empowering enterprises to boost efficiency and product quality simultaneously.
A mid-sized edible oil company in Southeast Asia transitioned from traditional cold-press to an integrated hot-press system. Within six months, the company noted:
These results underscore the strategic benefits of hot-press technology for scaling producers while suggesting the need for customization based on market positioning.

Effective SEO strategy for this topic revolves around keywords such as cold-press technology advantages, hot-press oil extraction efficiency, edible oil production technology, oilseed pressing machines, and energy-saving oil extraction equipment. Consistent inclusion of these phrases in website content, metadata, and anchor text significantly improves organic search visibility for target buyers.
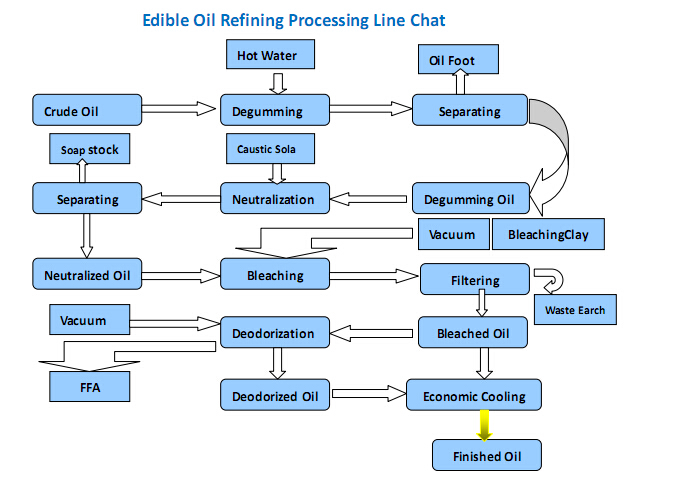
Leveraging advanced fully automated oilseed pressing equipment facilitates process standardization, minimizes human error, and optimizes energy consumption. Specifically, integrated cold and hot press units allow enterprises to custom tailor extraction parameters, addressing diverse oilseed characteristics and end-use market demands.
Investing in such technology not only boosts operational output by up to 20%, but also enhances brand reputation through consistent product quality and compliance with increasingly stringent food safety regulations.











