Wear-Resistant Component Maintenance Tips for Spiral Oil Press Machines: From Material Selection to Daily Care
2025-10-20
Application Tips
This article provides an in-depth analysis of wear-resistant components in spiral oil press machines, focusing on material selection and maintenance strategies. It highlights how hardness, toughness, and corrosion resistance impact the lifespan and operational stability of key parts such as the spiral shaft, cage, and vertical cake discharge mechanism. Through practical case studies, the article offers valuable insights to overseas users in food processing, chemical, and pharmaceutical industries, aiming to reduce maintenance frequency and downtime. Additionally, it outlines expert maintenance techniques paired with professional after-sales service support to help enterprises improve pressing efficiency and lower operational costs.

Maximizing Durability: Wear-Resistant Components Maintenance for Screw Oil Press Machines
In the demanding environments of food processing, chemical, and pharmaceutical industries, the performance and reliability of screw oil press machines hinge greatly on the wear resistance of their key components. This article delves deeply into how the choice of materials and maintenance practices for critical parts like the screw shaft, bearing cage, and vertical cake discharge mechanism influence equipment longevity and uptime, guiding overseas users towards cost-effective, high-efficiency production.
Understanding Wear-Resistant Materials: Hardness, Toughness, and Corrosion Resistance
Wear-resistant components are primarily evaluated based on three core material attributes:
- Hardness: A harder surface resists abrasive wear from raw materials; typically, materials with Rockwell hardness (HRC) between 50-60 offer optimal resistance without brittleness.
- Toughness: Ensures components endure impact and avoid cracking under mechanical stresses common in screw presses.
- Corrosion Resistance: Essential for parts exposed to moisture and oily compounds to prevent chemical degradation over time.
For example, high-chrome alloy steels with enhanced hardness (often HRC 55-58) combined with tempering treatments provide an excellent balance, delivering up to 30% longer service life than standard carbon steel counterparts.
Key Component Material Selection and Application
| Component |
Recommended Material |
Primary Benefit |
| Screw Shaft (Spiral Shaft) |
Chromium-Molybdenum Alloy Steel (HRC 55-58) |
Enhanced wear & corrosion resistance, reduces abrasive damage from raw seeds |
| Bearing Cage / Retainer |
Heat-treated High Carbon Steel |
Improved toughness and fatigue resistance under heavy dynamic loads |
| Vertical Cake Discharge Mechanism |
Surface-Hardened Stainless Steel |
Corrosion resistance and reduced friction wear from continuous cake discharge |
Maintenance Practices to Enhance Equipment Longevity
Regular maintenance rooted in scientific methodology can reduce repair costs by up to 25% and minimize unplanned downtime by 15%. The following protocols are pivotal:
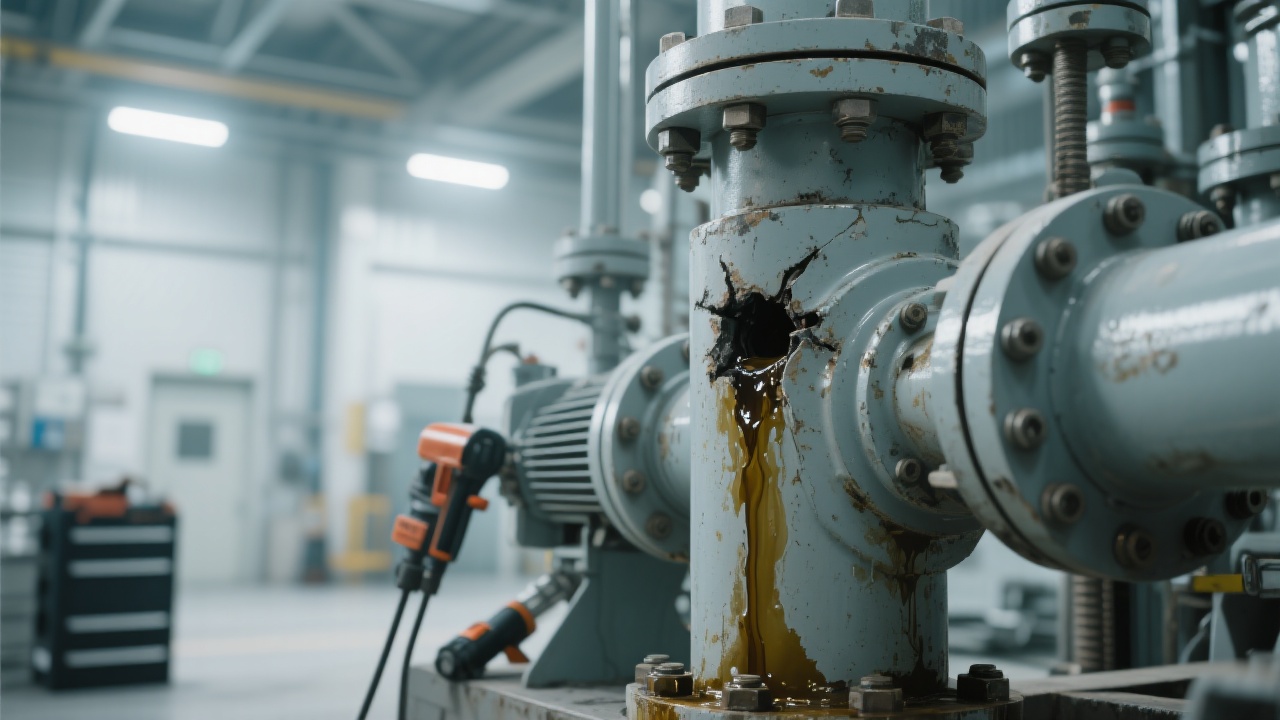
- Scheduled Inspection: Visual and tactile checks weekly to detect early signs of wear like grooves or cracking, especially on the screw shaft.
- Lubrication Management: Proper, timely lubrication of bearings and moving components reduces friction-induced wear by up to 40%.
- Cleaning Procedures: Removal of residual oil cakes and debris prevents corrosion and abnormal abrasion.
- Component Alignment: Ensuring precise alignment decreases mechanical stress on the cage and shaft, extending overall service life.
Case Study: Reducing Downtime with Enhanced Wear-Resistant Parts
One client in the food processing sector reported frequent breakdowns due to premature wear of their screw shafts and bearing cages. After upgrading to heat-treated chromium-molybdenum alloy steel components and implementing a structured maintenance schedule, the following improvements occurred over six months:
- Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) increased by 60%.
- Maintenance costs decreased by 18%, attributed to fewer replacements.
- Overall pressing efficiency rose by 12%, improving throughput.
This validated the crucial role that material selection tied with preventive care plays in maximizing operational uptime and lowering operational expenditures.
Practical Guidelines for Daily Operation
Operators should adopt these actionable tips:
- Check torque values and bearing temperatures to catch abnormal operation early.
- Record all inspections and maintenance intervals in logs to analyze wear trends.
- Train staff on identifying wear symptoms to enhance proactive maintenance.

Interactive FAQ to Clarify Common Inquiries
-
Q1: What is the lifespan difference between alloy steel and standard carbon steel parts?
-
Alloy steel parts typically last 1.3 to 1.5 times longer due to superior hardness and corrosion resistance, reducing overhaul frequency.
-
Q2: How often should bearings in the screw press be lubricated?
-
Lubricants should be applied every 200 operation hours or monthly, whichever occurs first, to maintain optimal motion and reduce wear.
-
Q3: Are there any recommended industry standards for wear-resistant materials?
-
Yes, materials conformed to ASTM A532 for abrasion-resistant castings and ISO 683 for heat-treated steels are preferred choices.






